Managing multiple medications isn’t just about remembering to take them-it’s about taking them at the right time, in the right order, and without clashing with each other. Every year, over 1.5 million people in the U.S. are harmed by medication errors, and nearly half of those happen because of poor scheduling. If you’re on five or more prescriptions, your risk of a dangerous drug interaction jumps to 82%. The good news? A simple, well-structured medication schedule can cut those risks dramatically.
Start with a Complete Medication List
Before you even think about timing, you need to know exactly what you’re taking. This includes prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen or antacids, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Many people forget that supplements can interact just like pills. For example, St. John’s Wort can make blood thinners like warfarin less effective, and calcium supplements can block thyroid medication if taken too close together. Write down every item with its name, dose, and why you take it. Don’t rely on memory. Bring this list to every doctor visit-even if you think you’ve told them before. A 2019 study found that pharmacists using a "brown bag" review (where patients bring all their meds in person) found an average of 3.2 discrepancies per patient. Verbal lists miss nearly 40% of medications.Use the Universal Medication Schedule (UMS) for Clear Timing
Forget vague instructions like "take twice daily" or "with meals." These lead to confusion, especially for older adults or those with low health literacy. The Universal Medication Schedule (UMS), developed by Northwestern University researchers, replaced vague terms with clear time blocks:- Morning: 6-10 a.m.
- Noon: 10 a.m.-2 p.m.
- Evening: 2-6 p.m.
- Bedtime: 8 p.m.-12 a.m.
Group Medications by Time Block to Avoid Clashes
Now that you have your list and clear time windows, start grouping. The goal is to avoid putting two drugs that interact into the same window. For example:- Antibiotics like ciprofloxacin shouldn’t be taken with calcium, iron, or antacids-space them at least 2 hours apart.
- NSAIDs like ibuprofen and blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin increase bleeding risk. If you must take both, stagger them-ibuprofen in the afternoon, aspirin in the morning.
- Thyroid meds like levothyroxine should be taken alone in the morning, with nothing else for at least 30 minutes.
- Diabetes meds like metformin can cause stomach upset if taken on an empty stomach. Pair them with breakfast or lunch.
Use a Pill Organizer-But Choose the Right One
A pill organizer isn’t just for seniors. If you take more than three pills a day, it’s a game-changer. A 2018 meta-analysis found that using a pill box with AM/PM or 7-day compartments reduces dosing errors by 45%. Don’t just grab the cheapest one. Look for:- Compartment labels (AM, PM, or specific times)
- Locking lids if you have kids or memory issues
- Large, easy-to-read text
- One that fits your schedule-some have 4 compartments per day for morning, noon, evening, bedtime
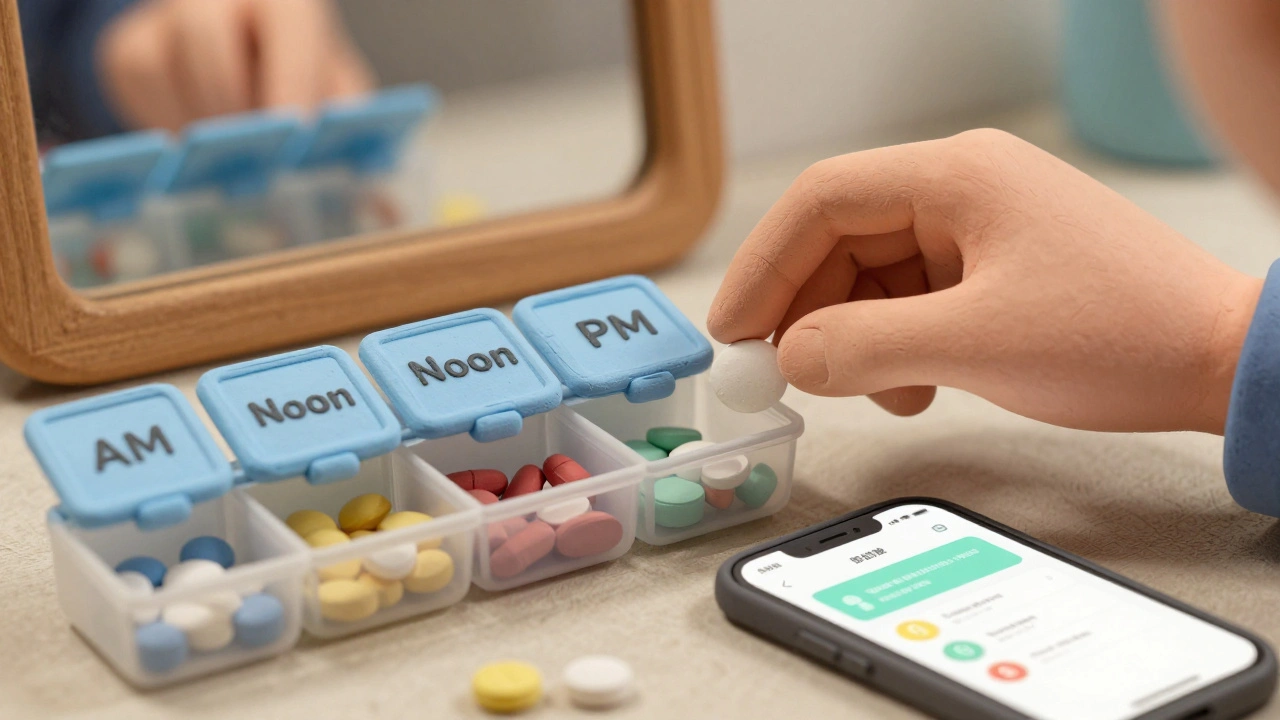

Sync Refills to Reduce Chaos
Having five different refill dates is a recipe for missed doses. The "90 x 4" method-getting 90-day supplies filled four times a year-saves time and reduces errors. Instead of juggling monthly refills, you get everything on the same day every three months. Talk to your pharmacist. Many pharmacies offer free refill synchronization. You’ll save trips, avoid running out, and reduce the chance of taking a drug too early or too late because you forgot to refill.Track and Adjust with a Medication Calendar
A pill organizer helps you take the right pill. A medication calendar helps you know what happened when. Use a simple notebook or printable calendar. Each day, check off when you took each pill. Note side effects: dizziness, nausea, unusual bruising, or fatigue. A 2020 case study followed a patient on 12 medications. After using a daily calendar and labeled pill boxes, their adverse events dropped from monthly to zero. This isn’t just about adherence-it’s about catching problems early. If you feel off after starting a new med, your calendar tells you exactly when it happened.Use Technology Wisely
Apps like Medisafe and MyTherapy send reminders and track interactions. A 2021 study showed they improve adherence by 20-35% compared to paper. But here’s the catch: only 38% of people over 65 use them consistently. If tech isn’t your thing, don’t force it. Paper calendars work for 72% of older adults, according to AHRQ. If you do use an app, make sure it lets you enter your exact UMS times and food requirements. Some apps only let you pick "morning" or "night"-not "take with lunch." That’s not enough.
Know the Red Flags
Some interactions are silent until they’re serious. Watch for:- Unexplained bruising or bleeding (possible blood thinner clash)
- Severe dizziness or fainting (could be blood pressure meds interacting)
- Upset stomach, diarrhea, or constipation (common with antibiotics and antacids)
- Confusion or memory issues (possible interaction with anticholinergics or benzodiazepines)
Work With Your Pharmacist
Your pharmacist is your best ally. They see all your meds at once. Most offer free medication therapy management (MTM) visits. During one, they’ll:- Review your full list
- Check for interactions
- Spot duplicates or unnecessary meds
- Suggest combination pills if you’re taking two separate drugs for the same condition
What If Your Doctors Give Conflicting Instructions?
It happens. One doctor says take your blood pressure pill in the morning. Another says take it at night. You’re not alone. A 2022 survey found 67% of patients with multiple specialists get conflicting timing advice. When this happens, don’t guess. Call your primary care provider or pharmacist and say: "I have conflicting instructions. Can you help me figure out the safest schedule?" They can coordinate with your specialists. You shouldn’t be the one playing medical detective.Stick With It-It Gets Easier
Building a schedule takes 2-4 weeks. The first week is the hardest. You’ll forget to fill your pill box. You’ll miss a dose. You’ll second-guess yourself. That’s normal. Set small goals: "This week, I’ll fill my pill box every Sunday." Then: "I’ll check my calendar every night." Soon, it becomes routine. And when you stop feeling dizzy, stop having stomach pain, or stop worrying you took the wrong pill-you’ll know it was worth it.What if I miss a dose of a medication that has interaction risks?
Don’t double up unless your doctor or pharmacist says to. If you miss a dose of a drug like warfarin or an antibiotic, check your medication guide or call your pharmacy. Some meds are safe to take late, others aren’t. Taking two at once could be dangerous, especially with blood thinners or seizure medications.
Can I take all my pills at once to make it easier?
No. Even if it feels convenient, mixing certain drugs can cause serious problems. For example, taking calcium and thyroid medication together can block absorption. Taking NSAIDs with blood thinners increases bleeding risk. Always follow the timing rules-even if you’re tired or in a rush.
Do I need to keep taking supplements if I’m on multiple medications?
Not necessarily. Many supplements don’t offer proven benefits and can interact with your meds. For example, magnesium can lower blood pressure too much when combined with certain heart meds. Vitamin K can interfere with warfarin. Ask your pharmacist to review your supplements. You might be able to stop some safely.
How do I know if a new medication will interact with what I’m already taking?
Always ask your pharmacist when a new prescription comes in. They use tools like Lexicomp that check for over 150 common interactions. Don’t rely on online searches-many are inaccurate or outdated. Your pharmacist has the latest, clinically validated data.
Are there any free tools I can use to track my meds?
Yes. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) offers free printable medication schedules and calendars online. You can also use a simple notebook or a free app like Medisafe (which has a free version). The key isn’t the tool-it’s consistency. Use what works for you.
If you’re managing multiple medications, you’re not alone. But you don’t have to manage it alone, either. With a clear schedule, a pill organizer, and a good relationship with your pharmacist, you can take control-without the fear of dangerous interactions.


Stephanie Fiero
December 5, 2025 AT 08:05i just take all my pills at once and hope for the best 😅 my pharmacist said i was gonna die but i told her i’ve been doing it for 7 years and still breathe
Laura Saye
December 5, 2025 AT 23:45There’s something deeply human about the ritual of medication - it’s not just chemistry, it’s a daily act of self-preservation. We’re not just managing drugs, we’re negotiating with time, with our bodies, with the quiet fear that one misstep could unravel everything. The UMS isn’t just a schedule - it’s a lifeline written in hours.
sean whitfield
December 7, 2025 AT 04:30Oh wow a 2020 study says this works. Next youll tell me water is wet and the sky is blue. Who funded this? Big Pharma? The pill company? The government? I dont trust any of them. I take my meds when the moon is in the 7th house.
Stephanie Bodde
December 7, 2025 AT 08:59You got this!! 💪 I started using a pill organizer last month and now I feel like a boss. No more panic at 2am wondering if I took my blood pressure pill. You’re not alone!! 🌟
Jennifer Patrician
December 9, 2025 AT 02:19This is all a scam. The government wants you dependent on pills so they can control you. Why do you think they make you take so many? They don't want you healthy. They want you docile. And that UMS? It's just another way to track you. Wake up.
Mellissa Landrum
December 10, 2025 AT 22:41my grandma took 12 pills a day and lived to 98. she never used no organizer. she just threw em in her mouth with a glass of coke. if it aint broke dont fix it. these apps and charts? thats for people who dont trust their own bodies.
Mark Curry
December 12, 2025 AT 20:26I’ve been using the UMS for 6 months now. It’s not perfect, but it’s the first time I haven’t felt like I’m playing Russian roulette with my meds. Small wins matter. I’m still learning, but I’m not scared anymore.
Manish Shankar
December 12, 2025 AT 21:42Respectfully, the approach outlined here is methodical and grounded in empirical evidence. The integration of the Universal Medication Schedule, coupled with pharmacist-led interventions, represents a paradigm shift in patient safety. One must acknowledge the systemic nature of medication errors and the efficacy of structured, standardized protocols in mitigating them.
luke newton
December 13, 2025 AT 08:47People like you think you’re helping, but you’re just feeding the machine. Why do you think your doctor gives you so many prescriptions? Because they get paid per pill. I’ve seen it. They don’t care if you live or die - they care about the next refill. You’re just a number on a spreadsheet.
an mo
December 13, 2025 AT 15:49Let’s be real - 82% interaction risk on 5+ meds? That’s statistically absurd. The CDC data is cherry-picked. They inflate numbers to push compliance tools and sell apps. Meanwhile, real polypharmacy chaos happens in nursing homes where staff are overworked. This post is a corporate wellness brochure dressed as medical advice.
aditya dixit
December 15, 2025 AT 08:40It’s not about the schedule - it’s about the silence between the pills. The quiet moments when you wonder if you’re healing or just surviving. I’ve been on six meds for five years. I don’t use apps. I write it down in a notebook with pen. It’s not fancy. But it’s mine.
Mark Ziegenbein
December 15, 2025 AT 23:43Look - I’ve read every peer-reviewed paper on polypharmacy since 2017. I’ve sat in three different MTM sessions. I’ve cross-referenced Lexicomp, Micromedex, and ClinicalKey. This article? It’s cute. It’s digestible. It’s designed for the 5th-grade health literacy demographic. But real medication management? It’s not about time blocks - it’s about pharmacokinetics, cytochrome P450 isoforms, renal clearance thresholds, and protein binding displacement. If you’re not consulting a clinical pharmacist who understands CYP3A4 inhibition, you’re just rearranging deck chairs on the Titanic.
Juliet Morgan
December 16, 2025 AT 21:41i used to forget everything… now i set 4 alarms and i color code my pills. its kinda fun? like a puzzle. and my anxiety dropped so much. you dont have to be perfect - just consistent. <3
Chris Brown
December 17, 2025 AT 04:06Why are we normalizing the idea that taking 10 pills a day is acceptable? This isn’t management - it’s surrender. We’ve turned medicine into a daily chore because we stopped asking why we need so many drugs in the first place. What happened to prevention? To diet? To exercise? This is just corporate medicine with a pretty checklist.
Michael Dioso
December 18, 2025 AT 16:25Oh wow so you’re telling me you can’t just mix ibuprofen with warfarin? Newsflash: I’ve been doing it for 10 years and my INR’s fine. You people are scared of your own shadows. Next you’ll say drinking water is dangerous if you’re on diuretics.
Stephanie Fiero
December 19, 2025 AT 00:26ok but what if your pharmacist is just trying to sell you a $40 pill box? i used a muffin tin and it worked fine. also i wrote "heart pill" on it with sharpie. no app needed.