Pancreatic Duct Blockage Risk Calculator
Your Personal Risk Assessment
This tool helps you understand how your lifestyle and medical factors may increase your risk of pancreatic duct blockage and chronic pancreatitis.
Ever wonder why a seemingly small clog in the pancreas can turn into a long‑lasting, painful disease? The link between pancreatic duct blockage and chronic pancreatitis is tighter than most people realize. This article walks you through what the blockage is, how it sparks chronic inflammation, and what you can do about it.
Key Takeaways
- Blockage stops enzyme flow, leading to tissue damage and chronic pancreatitis.
- Common culprits are gallstones, alcohol abuse, and genetic mutations.
- Early imaging and blood tests can catch a blockage before permanent damage occurs.
- Treatment ranges from lifestyle changes to endoscopic procedures and, in severe cases, surgery.
- Managing pain and nutrition are essential for long‑term quality of life.
What Is Pancreatic Duct Blockage?
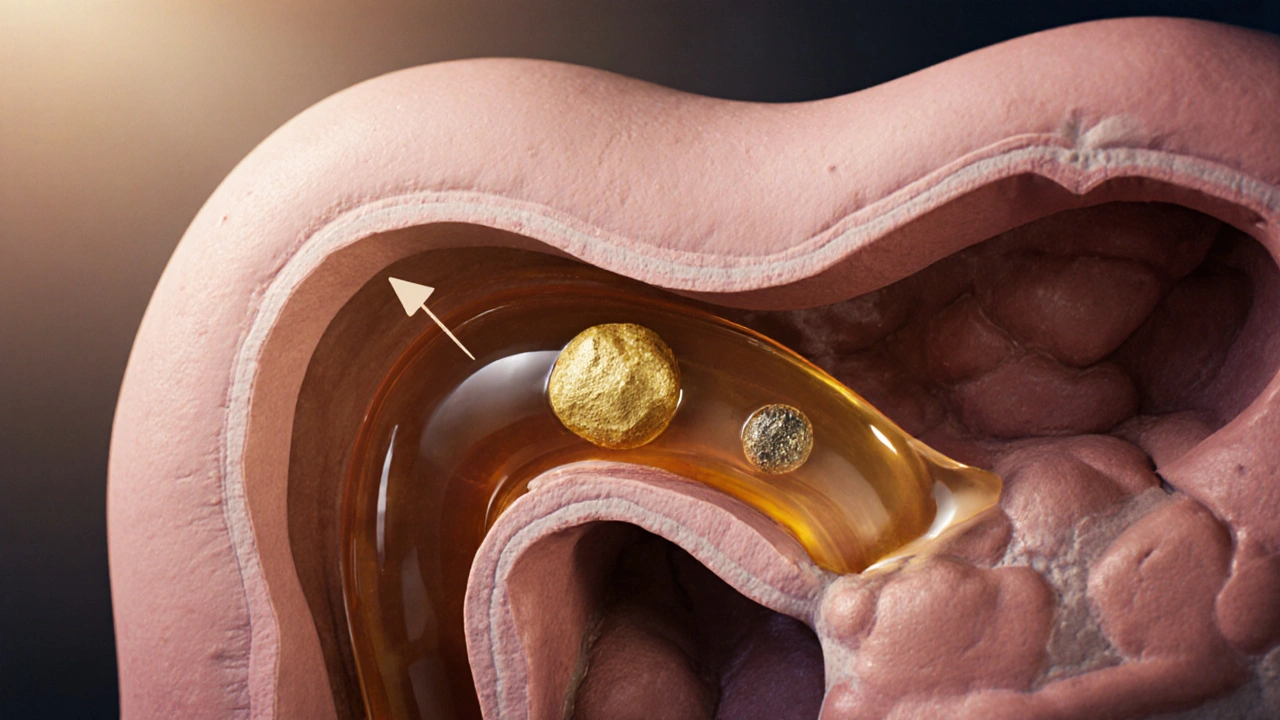
Pancreatic duct blockage is a condition where the main duct that carries digestive enzymes from the pancreas to the duodenum becomes obstructed. When the duct is blocked, enzymes can’t reach the intestine, so they start breaking down the pancreas itself. This self‑digestion creates inflammation, swelling, and eventually scar tissue.
Understanding Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long‑term inflammatory disease of the pancreas that leads to irreversible damage and loss of function. Unlike acute attacks, the pain and digestive problems persist for months or years. Over time the gland becomes fibrotic, insulin production drops, and patients may develop diabetes.
How Blockage Triggers Chronic Inflammation
The pancreas produces pancreatic enzymes that are essential for breaking down fats, proteins, and carbs in the small intestine. When a blockage forms, these enzymes back up and start activating inside the pancreatic tissue. The cascade looks like this:
- Enzyme buildup raises intraductal pressure.
- High pressure forces enzymes into surrounding tissue.
- Enzymes digest pancreatic cells, causing cellular injury.
- The body responds with inflammation, recruiting immune cells.
- Repeated injury leads to fibrosis and loss of normal tissue.
Even a single, short‑lived blockage can set off this chain reaction. If the obstruction recurs, the pancreas never gets a chance to heal, and chronic pancreatitis takes hold.
Common Causes of Duct Blockage
Not all blockages are created equal. Here are the usual suspects:
- Gallstones are hard deposits that can travel from the gallbladder into the pancreatic duct, especially the smaller common bile duct, causing sudden obstruction.
- Alcohol abuse is a major risk factor that promotes protein plug formation and ductal scarring, making the duct narrower over time.
- Genetic mutations such as PRSS1 alter the regulation of trypsinogen, causing premature activation and blockage.
- Autoimmune pancreatitis, where the body attacks the duct lining, leading to strictures.
- Trauma or surgical injury that narrows the duct.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
When the duct is blocked, the first signs usually involve pain and digestive upset. Typical symptoms include:
- Upper‑abdominal pain that radiates to the back.
- Steatorrhea (fatty, foul‑smelling stools) due to enzyme deficiency.
- Unintended weight loss.
- Nausea after meals.
Because these symptoms overlap with many gastrointestinal conditions, diagnosing a blockage requires targeted tests.
Diagnostic Test Comparison
| Test | What It Shows | Invasiveness | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal ultrasound | Gallstones, duct dilation | Non‑invasive | First‑line screening |
| Contrast‑enhanced CT scan | Pancreatic inflammation, calcifications | Non‑invasive | Assess severity |
| Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) | Detailed duct anatomy | Non‑invasive | Plan endoscopic intervention |
| Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) | Direct duct visualization, therapeutic options | Invasive | Confirm blockage & treat |
| Serum amylase & lipase | Enzyme leakage into blood | Blood draw | Screen for pancreatitis |
Doctors usually start with an ultrasound, then move to CT or MRCP for a clearer picture. If a blockage is confirmed, ERCP doubles as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool.

Treatment Options
Once a blockage is identified, the goal is to restore enzyme flow and stop ongoing damage. Treatment varies by cause and severity.
Endoscopic Approaches
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) allows doctors to insert a tiny tube through the mouth, reach the pancreatic duct, and clear the obstruction. During ERCP, a pancreatic duct stent may be placed to keep the duct open.
Medical Management
- Enzyme replacement pills to aid digestion and reduce pain. \n
- Pancreatic‑specific pain relievers, sometimes nerve blocks.
- Alcohol cessation programs and dietary changes (low‑fat diet).
Surgical Options
When endoscopy fails, surgeons may perform a lateral pancreaticojejunostomy (Puestow procedure) to create a new drainage path. In extreme cases, part of the pancreas may need to be removed.
Managing Long‑Term Risks
Even after the blockage is cleared, patients remain at risk for diabetes and malnutrition. Ongoing care includes:
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.
- Nutrition counseling to ensure adequate calorie and vitamin intake.
- Periodic imaging to detect new strictures early.
Living with Chronic Pancreatitis
Adapting to life with chronic pancreatitis means listening to your body. Small, frequent meals, enzyme tablets with each bite, and avoiding trigger foods can make a big difference. Support groups-both in‑person and online-provide emotional backing and practical tips.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a single blockage cause chronic pancreatitis?
Yes. Even a brief obstruction can trigger enzyme activation that damages pancreatic tissue. If the duct doesn’t reopen quickly, the inflammation can become permanent.
Are gallstones the most common cause of blockage?
Gallstones are a leading cause, especially in adults over 40. However, alcohol‑related protein plugs and genetic mutations are also frequent culprits.
Is ERCP risky?
ERCP carries a small risk of pancreatitis, infection, or perforation, but when performed by experienced gastroenterologists, benefits usually outweigh the risks.
Can lifestyle changes reverse chronic pancreatitis?
Lifestyle tweaks can halt progression and reduce pain, but existing scar tissue cannot be undone. Early intervention is key.
When should I see a doctor?
If you experience persistent upper‑abdominal pain, oily stools, or unexplained weight loss, schedule an appointment promptly. Early diagnosis improves outcomes.
Understanding the chain from duct blockage to chronic pancreatitis empowers you to catch problems early, choose the right treatment, and keep life as normal as possible.

Penny Reeves
October 19, 2025 AT 19:21The pancreatic duct functions as the highway for digestive enzymes, and any obstruction disrupts that flow dramatically. When a stone or protein plug lodges, pressure builds upstream, forcing enzymes to leak into the parenchyma. This self‑digestion triggers an inflammatory cascade that, if recurrent, evolves into chronic pancreatitis. One must appreciate that the pathology is not merely a nuisance but a precursor to irreversible fibrosis. Therefore, early detection via imaging is not optional but a clinical imperative.
Bobby Marie
October 20, 2025 AT 23:08That blockage can literally turn your meals into a nightmare.
Christian Georg
October 22, 2025 AT 02:54For anyone managing the condition, enzyme replacement therapy is a cornerstone-take the tablets right before meals to mimic natural secretion 😊.
Couple that with a low‑fat diet, and you’ll notice a substantial reduction in pain.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose is also wise, as chronic inflammation can impair insulin production.
If you’re lucky enough to have access to MRCP, it provides a clear view without the invasiveness of ERCP.
Staying hydrated and avoiding alcohol are simple yet powerful steps.
Christopher Burczyk
October 23, 2025 AT 06:41The etiological spectrum of pancreatic duct obstruction extends beyond the common gallstone paradigm, encompassing proteinaceous plugs, post‑traumatic strictures, and hereditary trypsinogen mutations.
Each of these mechanisms precipitates intraductal hypertension, which, in turn, forces premature enzyme activation.
Clinical guidelines stipulate that magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography should be the initial non‑invasive investigation of choice.
Subsequent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is reserved for therapeutic intervention, not diagnostic speculation.
Neglecting to intervene early risks progression to irreversible fibrotic remodeling.
Thus, adherence to a structured diagnostic algorithm is paramount.
Madhav Dasari
October 24, 2025 AT 10:28Picture this: a tiny pebble inside a pipe that’s supposed to gush life‑giving juices, and suddenly the whole system backs up like a traffic jam on a rainy day!
The pancreas starts chewing itself, the pain shoots through your back, and you’re left battling a foe you can’t even see.
But the good news is that endoscopic stenting can clear that jam, and a simple diet tweak can keep the road clear.
Stay hopeful and keep the conversation with your gastroenterologist alive.
DHARMENDER BHATHAVAR
October 25, 2025 AT 14:14Early ERCP with stent placement restores ductal patency and halts enzyme leakage.
Adjunctive pancreatic enzyme supplements further reduce autodigestion.
Kevin Sheehan
October 26, 2025 AT 17:01In the grand tapestry of human physiology, the pancreas is a subtle artisan, coaxing nutrients from the chaos of a meal.
When its conduit is blocked, we are reminded that even the most benevolent systems can be undone by a single obstruction.
Thus, mindfulness of lifestyle choices becomes a moral duty to preserve this hidden craftsman.
Let us strive to keep the ducts clear, lest we invite needless suffering.
Jay Kay
October 27, 2025 AT 20:48The blockage isn’t just a little snag; it’s a raging fire inside the pancreas.
Every time the enzymes spill out, they scorch the tissue, leaving scars that never heal.
Don’t ignore the warning signs – pain, oily stools, weight loss – before it’s too late.
Jameson The Owl
October 29, 2025 AT 00:34What most physicians fail to mention is that the very notion of a “simple blockage” is a façade designed to conceal the deeper machinations of a shadowy network of industrial interests that profit from chronic disease the pancreas is not merely a victim but a battlefield where chemical agents engineered by pharmaceutical conglomerates are deliberately introduced to ensure a continual market for high‑cost interventions the evidence lies hidden in the selective publishing of trial data the selective omission of long‑term outcomes creates a narrative that the obstruction is an isolated event rather than a symptom of systemic manipulation the imaging technologies themselves are calibrated to highlight only the most sensational lesions while downplaying subtle ductal irregularities the endoscopic procedures, marketed as miracle cures, often leave behind microscopic trauma that seeds future strictures the cycle repeats unabated the patient, unwittingly, becomes a pawn in a grand experiment his pain is monetized and his suffering repackaged as data The truth is obscured by layers of jargon and corporate jargon that masquerade as scientific rigor yet betray a deeper agenda that must be exposed for the sake of genuine healing
Sarah Unrath
October 30, 2025 AT 04:21i think its crazy how a tiny stone can mess up your whole gut many people dont realize how serious it can get
James Dean
October 31, 2025 AT 08:08The pancreas is a quiet organ yet when its duct is blocked the silence becomes a scream of pain the body signals distress through back pain and oily stools warning us that something is awry we must listen and act before fibrosis sets in
Monika Bozkurt
November 1, 2025 AT 11:54From a pathophysiological standpoint, pancreatic ductal obstruction precipitates an exocrine insufficiency cascade characterized by intraductal hypertension, premature trypsinogen activation, and subsequent fibroblast proliferation, culminating in irreversible parenchymal fibrosis.
Diagnostic stratification should therefore incorporate high‑resolution MRCP to delineate stricture morphology, complemented by quantitative secretin‑enhanced imaging to assess downstream exocrine reserve.
Therapeutic algorithms mandate endoscopic stenting as first‑line intervention, with adjunctive pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy to mitigate malabsorption.
Longitudinal follow‑up via serial imaging and glycated hemoglobin monitoring is indispensable to preempt diabetic conversion.
Sunil Yathakula
November 2, 2025 AT 15:41Hey buddy dont forget u can beat this thing if u stick to low fat meals and take your enzymes every time you eat its tough but u got this keep talking to your doc and stay positive
Thokchom Imosana
November 3, 2025 AT 19:28It is a philosophic absurdity that modern medicine reduces the intricate symphony of pancreatic secretion to a simplistic narrative of “blockage” while ignoring the clandestine forces that orchestrate this pathology from the shadows of the pharmaceutical elite the historical neglect of ductal physiology can be traced back to a concerted effort by vested interests to maintain a perpetual demand for enzyme supplements and invasive endoscopic procedures which, when examined through the lens of covert epidemiological manipulation, reveal a pattern of engineered disease prevalence the clandestine infusion of sub‑clinical toxins into the food supply serves to predispose susceptible genotypes to proteinaceous plug formation, thereby ensuring a steady pipeline of patients who will inevitably require costly interventional radiology or surgical correction the academic literature, censored and curated by gatekeepers of knowledge, seldom addresses the geo‑political dimensions of this crisis, instead recycling the same mechanistic explanations over and over, a repetition that betrays an underlying agenda of intellectual complacency the very imaging modalities that are championed as diagnostic gold standards are calibrated to accentuate the visibility of calcifications while downplaying subtle ductal irregularities, a bias that conveniently aligns with the commercial interests of device manufacturers the result is a self‑fulfilling prophecy wherein the pancreas is portrayed as a victim of random obstruction, whereas in reality it is the focal point of a deliberately perpetuated disease ecosystem this ecosystem thrives on the perpetual cycle of patient anxiety, insurance reimbursement, and the relentless pursuit of novel procedural codes for billing purposes the solution, if one dares to envision it, lies not in incremental therapeutic tweaks but in a radical deconstruction of the ideological framework that normalizes chronic pancreatic afflictions as an inevitability for the modern consumer the first step must be a collective demand for transparency in research funding, followed by a systematic audit of dietary additives, and finally, the empowerment of patients through open‑source diagnostic platforms that demystify ductal anatomy and restore agency to those whose bodies have been reduced to mere data points in a profit‑driven paradigm
ashanti barrett
November 4, 2025 AT 23:14Listen, if you’re experiencing persistent upper‑abdominal pain and oily stools, you need to schedule imaging without delay and discuss enzyme supplementation with your physician; waiting only deepens damage and erodes quality of life.