When your immune system mistakenly targets the insulin-making cells in your pancreas, you’re dealing with autoimmune diabetes, a condition where the body’s defense system destroys the beta cells that produce insulin. Also known as type 1 diabetes, it’s not caused by diet or lifestyle—it’s an internal mistake your body makes, often starting in childhood or young adulthood. Unlike type 2 diabetes, where insulin resistance is the main issue, autoimmune diabetes means your body simply stops making insulin. Without it, glucose can’t enter your cells for energy, and blood sugar climbs dangerously high.
This condition requires lifelong insulin therapy because your pancreas can’t recover those lost cells. People with autoimmune diabetes must monitor blood sugar multiple times a day, count carbs, and adjust insulin doses based on food, activity, and stress. It’s not just about shots or pumps—it’s a constant balancing act. Many also deal with related issues like thyroid disorders or celiac disease, since autoimmune conditions often cluster together. If your body attacks one system, it’s more likely to target others. That’s why doctors check for other autoimmune markers when someone is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
The triggers aren’t fully understood, but genetics play a role, and certain viruses may set off the immune response in people who are already at risk. There’s no cure yet, but research is moving fast. New treatments aim to slow or stop the immune attack early, preserve remaining insulin production, and even reset the immune system. For now, the focus stays on managing the condition to avoid complications like nerve damage, kidney problems, or eye disease. The good news? With careful control, people with autoimmune diabetes live full, active lives.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides on related topics: how steroids like dexamethasone affect blood sugar, how insulin glargine works compared to other long-acting options, and how drug interactions can complicate diabetes care. These aren’t just theory—they’re tools people use every day to stay healthy.
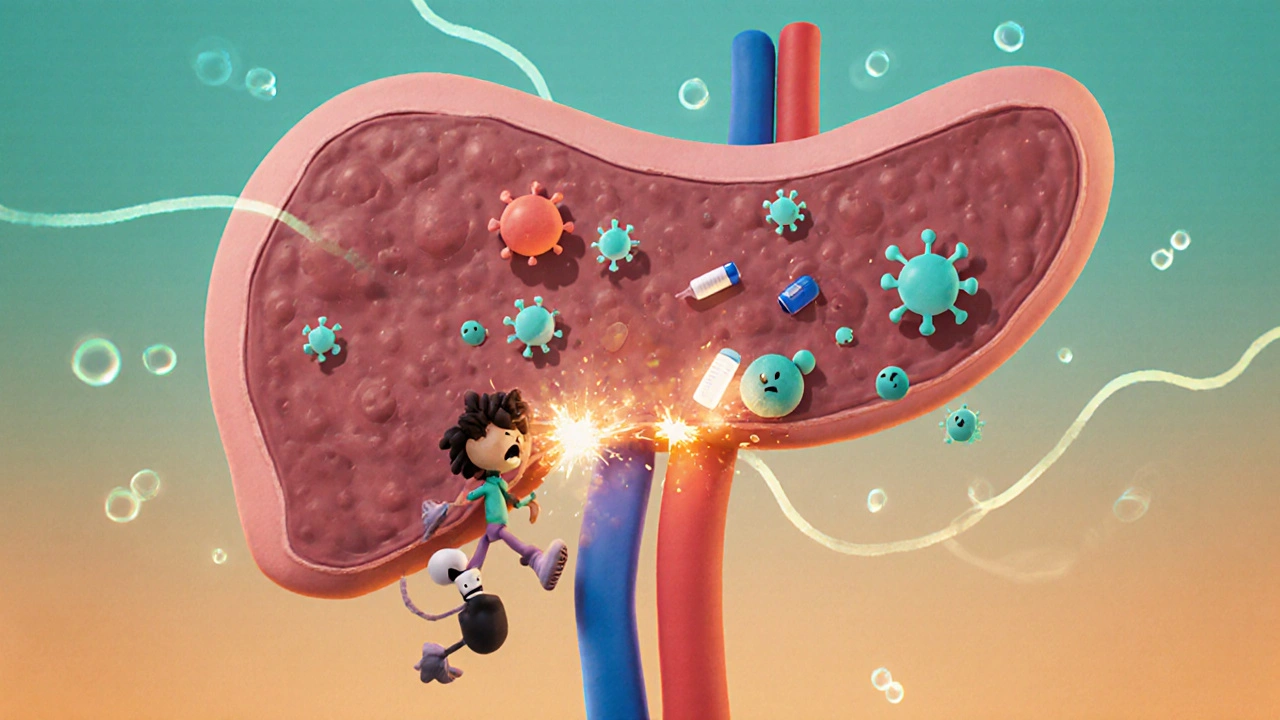
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Learn how it develops, why insulin is essential, and what new treatments like teplizumab and stem cell therapy are changing the future of management.
Nov 13 2025
Menu