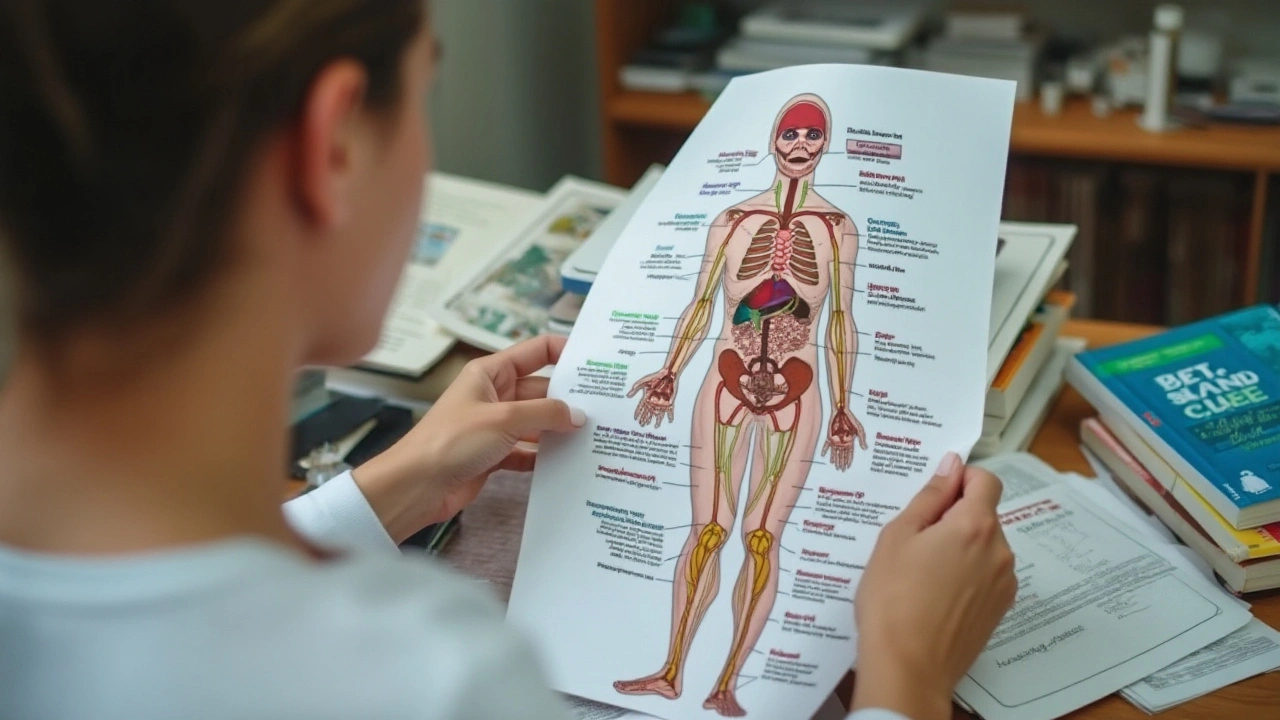
Enzymes often go unnoticed, yet they play a crucial role in our well-being. They are like the unsung heroes behind the scenes, making sure our body functions as it should. While most people associate enzymes with digestion, they are also essential for other bodily functions, including hormonal health.
Without enough enzymes, the body's hormone levels can become unbalanced, leading to various health issues. This can be particularly concerning as hormones regulate many vital processes such as mood, metabolism, and reproductive health. Understanding how enzyme deficiency impacts hormonal balance can help us take proactive steps to improve our overall well-being.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how enzymes and hormones interact, identify the symptoms of enzyme deficiency, and offer practical advice on how to boost enzyme levels naturally.
- Understanding Enzymes and Hormones
- The Role of Enzymes in Hormonal Balance
- Symptoms of Enzyme Deficiency and Hormonal Imbalance
- Ways to Boost Enzyme Levels
- Practical Tips for Maintaining Hormonal Health
Understanding Enzymes and Hormones
To truly grasp the connection between enzyme deficiency and hormonal imbalance, it's essential to first understand what enzymes and hormones are and how they function in the body. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts in various biochemical reactions, meaning they speed up these reactions without being consumed themselves. Our bodies produce enzymes to aid in digestion, energy production, detoxification, and hormone regulation, among other tasks.
On the other hand, hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to tissues and organs. They work slowly, over time, and affect many different processes, including growth and development, metabolism, sexual function, reproduction, and mood. Hormones are secreted by various glands in the endocrine system, such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas.
The interplay between enzymes and hormones is intricate and crucial for maintaining optimal health. Specific enzymes are responsible for synthesizing, activating, and breaking down hormones. For example, the enzyme aromatase converts androgens into estrogens, a process critical for regulating sexual development and reproductive functions. A lack of this enzyme can lead to significant hormonal imbalances.
The Role of Enzymes in Hormone Regulation
Enzymes play several critical roles in hormone regulation. They help synthesize hormones from their precursor molecules, activate hormones that are initially inactive, and degrade hormones to ensure they do not remain in the body longer than necessary. Take the enzyme 11-beta-hydroxylase, for instance; it is vital for the production of cortisol, a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels, regulate metabolism, and reduce inflammation. Deficiency in this enzyme can lead to adrenal insufficiency.
When the body does not produce enough of certain enzymes, hormonal pathways can become disrupted. This disruption can manifest in many ways, such as unexplained weight gain, fatigue, mood swings, and reproductive issues. A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism indicated that enzyme deficiencies are often linked to hormonal disorders like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and adrenal hyperplasia.
"Hormonal imbalances can stem from various factors including enzyme deficiencies. Recognizing and addressing these deficiencies can have a profound impact on an individual's quality of life," says Dr. Samantha Blake, an endocrinologist at the University of Manchester.
The Symptoms of Enzyme Deficiency
Identifying enzyme deficiency is not always straightforward, as the symptoms can be subtle and easily mistaken for other conditions. Common indicators include digestive problems, such as bloating, gas, and indigestion. Enzyme deficiencies can also manifest through non-digestive symptoms like chronic fatigue, mood disorders, and issues related to reproductive health. For example, women with low levels of the enzyme lactase may also experience hormonal symptoms such as irregular menstrual cycles.
The good news is that through proper diagnosis and treatment, enzyme deficiencies can be managed. Addressing these deficiencies often involves dietary changes, enzyme supplements, and lifestyle modifications. It's crucial to consult healthcare professionals who can provide a tailored approach based on individual needs and conditions.
Understanding the vital roles that enzymes play in hormone regulation is the first step towards better health. By recognizing the signs of enzyme deficiency early and taking actionable steps to boost enzyme levels, we can help restore balance and improve overall well-being.
The Role of Enzymes in Hormonal Balance
Enzymes are essential for the body’s metabolic processes, which includes the synthesis and regulation of hormones. Simply put, enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions in our body. Without these catalysts, many of the reactions necessary for maintaining life, including those that regulate hormone levels, would occur too slowly. This can lead to various health problems.
Hormones act as chemical messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to tissues and organs. They help regulate everything from growth and metabolism to mood and reproductive functions. However, the production and release of these hormones depend heavily on specific enzymes. For instance, the enzyme aromatase is crucial for converting androgens (male hormones) into estrogens (female hormones). Any deficiency in aromatase can result in an imbalance between these hormones, leading to a plethora of issues such as mood swings, hot flashes, and even infertility.
Another important enzyme is 21-hydroxylase, which plays a pivotal role in the production of cortisol and aldosterone produced by the adrenal glands. Cortisol is often called the 'stress hormone' because it helps the body respond to stress. Aldosterone helps control blood pressure by managing the balance of sodium and potassium in our bodies. A deficiency in 21-hydroxylase can lead to adrenal insufficiency, causing symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and low blood pressure.
Research has shown that enzyme deficiencies can also impact insulin regulation. Insulin is a hormone that allows cells to take in glucose for energy. Enzymes like glucokinase and hexokinase are involved in the metabolism of glucose. A lack of these enzymes can impair the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to conditions like diabetes. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, enzymes are critical in maintaining balanced hormone levels and disruptions can have widespread effects on the body.
"Enzymes serve not just as biological catalysts but are indispensable to the hormonal equilibrium in the human body." - Dr. Sarah Spencer, Endocrinologist at the Institute of Metabolic Science
Proper enzyme function is vital for breaking down the food we eat into the nutrients our bodies need to produce hormones. Digestive enzymes like proteases, lipases, and amylases help in breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, respectively. Without these digestive enzymes, our bodies would struggle to absorb essential nutrients, which could eventually disrupt hormonal balance. For example, inadequate absorption of fats can affect the production of steroid hormones, which are derived from cholesterol.
Furthermore, the liver, which acts as the body's detoxifier, relies on enzymes like cytochrome P450 to metabolize hormones and toxins. If these enzymes are deficient or overwhelmed, it can lead to a buildup of toxins and hormonal imbalances. This underscores the interconnectedness of various bodily functions and the pivotal role enzymes play in maintaining overall hormonal health.
To sum up, enzymes are fundamental to maintaining hormonal balance. They are involved in the synthesis, activation, and deactivation of hormones, and a deficiency in these enzymes can lead to various health issues. Being aware of the importance of enzymes and ensuring optimal levels through diet and lifestyle choices can significantly contribute to better hormonal health.

Symptoms of Enzyme Deficiency and Hormonal Imbalance
Recognizing the symptoms of enzyme deficiency and its impact on hormonal balance can be quite challenging. The signs are often subtle and can easily be mistaken for other health issues. Nonetheless, paying attention to your body and understanding the critical role enzymes play can help in identifying the problem early on.
One of the first things you might notice is chronic fatigue and low energy levels. Without sufficient enzymes, your body struggles to break down and absorb nutrients efficiently. This can lead to constant tiredness, making it hard to get through the day. For instance, someone who lacks enzymes necessary for thyroid hormone production may feel perpetually exhausted.
Digestive issues are another common symptom. This includes bloating, gas, and frequent indigestion. Enzymes are crucial for breaking down food and extracting nutrients. A deficit in them can cause improper digestion, making you uncomfortable after meals. It can even lead to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Hormonal imbalances often manifest in mood swings and emotional instability. Enzymes help produce and regulate hormones like serotonin and dopamine. When these are out of whack, you might experience sudden mood changes, anxiety, or even depression. Women may also notice irregular menstrual cycles or severe PMS symptoms due to hormonal imbalances.
In some cases, weight gain or difficulty in losing weight can be a red flag. Hormones like insulin and cortisol play a part in regulating your metabolism. Enzyme deficiency can throw these hormones off balance, making weight management a struggle despite a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
Skin problems can also be a tell-tale sign. Acne, eczema, and other skin conditions can flare up due to hormonal imbalances caused by enzyme deficiency. Your skin reflects your internal health, and when your body is not producing enough enzymes, it often shows on your skin.
According to Dr. Michael Murray, a leading expert in natural health, "Enzyme deficiency often goes unnoticed until more severe symptoms arise, but paying attention to these early signs can make a significant difference in long-term health."
Headaches and migraines are less obvious, yet significant, symptoms. Enzyme deficiencies can disrupt the balance of hormones like estrogen and progesterone, particularly in women. This can lead to frequent headaches or migraines, often around the menstrual cycle.
Finally, a weakened immune system is a serious concern. Enzymes contribute to various immune system processes. Without them, you may find yourself more susceptible to infections, colds, and other illnesses. Your body’s ability to fight off pathogens diminishes, leaving you feeling run down more often.
Being aware of these symptoms can help you take action to address enzyme deficiencies. Incorporating more enzyme-rich foods into your diet or discussing enzyme supplementation with a healthcare provider are proactive steps you can take. By doing so, you can help restore hormonal balance and improve your overall well-being.
Ways to Boost Enzyme Levels
Boosting your enzyme levels stands at the foundation of promoting proper health and supporting hormonal balance. There are several natural and practical ways to ensure your body gets the enzymes it needs to function optimally. By incorporating specific dietary changes and lifestyle habits, you can significantly enhance your enzyme levels, which in turn can help maintain healthy body functions.
One of the most effective ways to boost enzyme levels is by eating more raw fruits and vegetables. These foods are naturally rich in enzymes. For instance, pineapples contain bromelain which helps break down proteins, while papayas boast an enzyme called papain that aids digestion. Incorporating a variety of raw foods in your meals ensures you benefit from a diverse range of enzymes.
Another beneficial approach is to include fermented foods in your diet. Fermented foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi are excellent sources of natural enzymes and probiotics. These foods not only help in breaking down food particles but also positively influence your gut health, creating a more conducive environment for enzyme production.
Paying attention to how you eat is equally important. Taking time to chew your food thoroughly stimulates saliva production, which is rich in digestive enzymes. This simple habit can significantly improve digestion and nutrient absorption. Slow eating also signals your brain that you are full, helping to prevent overeating, which can burden your digestive system.
Staying hydrated is another critical factor in supporting enzyme activity. Water plays a vital role in the biochemical reactions that involve enzymes. Dehydration can hamper these reactions, reducing enzyme efficacy. Drinking enough water throughout the day ensures that your body maintains an environment where enzymes can function optimally.
Reducing your intake of highly processed foods is also crucial. These foods often have added preservatives that can inhibit enzyme activity. They are also typically low in nutritional value, providing little to no enzymes. Focusing on whole, minimally processed foods boosts your enzyme levels and provides necessary nutrients that support overall health.
For those looking to give their enzyme levels an extra push, considering enzyme supplements can be a viable option. These supplements can help compensate for any enzyme deficiencies and support better digestion and absorption of nutrients. However, always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen to ensure it fits your health needs.
Dr. Michael Murray, a naturopathic doctor, states, "Digestive enzymes are crucial for the efficient breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients. Supporting your body with enzyme-rich foods and, when necessary, supplements can significantly improve digestive health and overall wellbeing."
Regular exercise is often overlooked, but it can stimulate enzyme activity in your body. Physical activity enhances blood flow, which can help transport enzymes to different parts of your body where they are needed. A consistent exercise routine, even if it’s just walking regularly, can make a considerable difference in enzyme activity and hormonal balance.
Taking care of your stress levels is just as important as a balanced diet and regular exercise. Stress can impact enzyme production negatively, so finding ways to relax and manage stress can support your enzyme health. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and even hobbies can help lower stress and improve overall enzyme function.
In summary, improving your enzyme levels involves a multifaceted approach that combines dietary choices, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes the use of supplements. By eating more raw and fermented foods, staying hydrated, and practicing mindfulness, you can have a significant positive impact on your enzyme levels and overall health. These changes are simple yet powerful ways to support your body's natural functions and achieve better hormonal balance.

Practical Tips for Maintaining Hormonal Health
Maintaining hormonal health can often feel like a balancing act. Our modern lifestyle, with its demands and dietary habits, can easily disrupt this balance. However, there are several practical steps you can take to support your hormone levels and ensure that your body has the enzymes it needs to function optimally.
A healthy, balanced diet is the cornerstone of hormonal health. Eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods ensures that you get all the vitamins and minerals essential for hormone production and activation. Incorporate plenty of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Foods rich in zinc, magnesium, and B vitamins, such as seeds, nuts, fish, and leafy greens, play a significant role in enzyme production and hormone regulation.
Hydration is another crucial but often overlooked aspect of maintaining hormonal balance. Water is essential for nearly all bodily functions, including enzyme activity. Drinking enough water helps to flush out toxins, supports metabolic processes, and keeps your cells functioning correctly. Aim for at least eight glasses a day, and remember that caffeinated or sugary beverages do not count towards this total.
Getting enough sleep is vital for both enzyme and hormone health. During sleep, the body undergoes numerous processes that restore and repair cells, balance hormones, and produce essential enzymes. Make sure you're getting seven to eight hours of quality sleep every night. Establishing a consistent sleep routine, reducing screen time before bed, and creating a restful environment can all help improve sleep quality.
Stress management is also vital for hormonal balance. Chronic stress can lead to a surge of cortisol, the stress hormone, which can interfere with the function of other hormones in your body. Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and even regular walks can help keep cortisol levels in check. As Dr. Ashley Koff, a reputable nutrition expert, once said:
"Managing stress is as important as maintaining a healthy diet when it comes to taking care of your hormonal health."
Regular physical activity is another essential aspect of maintaining hormonal health. Exercise helps regulate insulin, which is a key hormone involved in managing blood sugar levels. It also supports the production and balance of other hormones, such as endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise five times a week. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and strength training can be particularly effective.
If you suspect an enzyme deficiency is contributing to your hormonal imbalance, consider talking to a healthcare provider about enzyme supplements. There are various supplements available that can aid digestion and improve enzyme levels. However, it's essential to consult a medical professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your specific needs.
Finally, limiting exposure to endocrine disruptors such as certain plastics, pesticides, and personal care products can help maintain hormonal balance. These substances can interfere with hormone functions and enzyme activities, so opting for natural and organic products whenever possible is a good practice.
In summary, supporting hormonal health through a balanced diet, adequate hydration, quality sleep, stress management, regular exercise, and mindful lifestyle choices can make a significant difference. Take small but consistent steps and listen to your body. Maintaining the right balance might not be as difficult as it seems.

Alissa DeRouchie
September 20, 2024 AT 20:59God I wish people would stop treating enzymes like they’re some mystical unicorns that magically fix everything – sure they’re important, but not every gut‑issue is a cosmic conspiracy. The article throws around “unsung heroes” like it’s a superhero movie and I’m over it. Look, we know enzymes help with digestion and hormone synthesis, but you can’t blame every mood swing on a missing enzyme. There’s genetics, lifestyle, stress, all that jazz – not just a low‑enzyme vibe. So yeah, boost your pineapple, but don’t expect it to turn you into a zen master overnight.
Emma Howard
September 29, 2024 AT 13:19Absolutely love the practical tips! 🍎 Adding raw fruits like pineapple and papaya is such an easy win. Keep chewing your food – it really does spark saliva enzymes. Hydration is key, so drink up! And seriously, ditch the processed stuff – your hormones will thank you. Let’s keep each other motivated on this enzyme journey!!
dee gillette
October 8, 2024 AT 05:39While the article presents a comprehensive overview, it arguably overstates the causal link between enzyme deficiency and hormonal disorders. Empirical evidence suggests a multifactorial etiology, where enzymes represent merely one component of a broader metabolic network. Therefore, readers should interpret the recommendations with measured skepticism.
Jasin P.
October 16, 2024 AT 21:59Oh great, another “miracle” post about enzymes fixing your life. Yeah, because my cortisol never spikes after a bad coffee, right? If only a little bit of bromelain could stop the government from meddling with our hormones. Spoiler: it won’t. But hey, keep selling the dream – maybe one day the “enzyme gods” will actually answer.
Lily Đàn bà
October 25, 2024 AT 14:19Honestly, this whole piece reads like patriotic propaganda for the health industry. It’s as if they’re saying, “America, eat more raw fruit and we’ll fix all your hormonal woes!” Meanwhile, real issues like environmental toxins are ignored. Stop glorifying enzymes as a national cure‑all and start addressing the bigger picture.
Joseph O'Sullivan
November 3, 2024 AT 05:39Interesting take, but let’s not forget that enzymes are micro‑tools, not the master architects of our endocrine system. While raw foods add value, the body’s own regulatory loops are far more sophisticated than just a handful of fruit‑derived catalysts. So, yeah, enjoy the bromelain, but don’t hand over the reins of hormonal health to a pineapple slice.
Conor McCandless
November 11, 2024 AT 21:59When we examine the intricate cascade of biochemical pathways that underpin hormonal equilibrium, it becomes evident that enzymes occupy a position of undeniable significance, serving as catalytic agents that accelerate the conversion of precursors into active hormones, thereby ensuring the seamless progression of physiological processes.
Take, for instance, the enzyme aromatase, a pivotal player in the biosynthesis of estrogen from androgenic substrates; a deficiency here can precipitate a cascade of downstream effects, manifesting in both metabolic and reproductive disturbances.
Furthermore, the enzyme 21‑hydroxylase, essential for cortisol and aldosterone synthesis, exemplifies how enzymatic insufficiency can culminate in adrenal insufficiency, with clinical presentations ranging from chronic fatigue to electrolyte imbalances.
The interdependence between enzymatic activity and hormonal feedback loops cannot be overstated, as each hormone exerts regulatory control over enzyme expression, creating a dynamic reciprocity that sustains homeostasis.
In the context of insulin regulation, glucokinase and hexokinase act as gatekeepers of glucose utilization, underscoring the role of enzymes in modulating glycemic control, and thereby influencing adipose tissue distribution and energy balance.
Moreover, the gastrointestinal milieu, enriched with proteases, lipases, and amylases, is crucial for the breakdown of macronutrients, ultimately providing the amino acids and fatty acids required for steroid hormone biosynthesis.
Consider also the hepatic cytochrome P450 system, a family of enzymes tasked with the oxidation and clearance of both endogenous hormones and xenobiotics, whose impairment can result in hormonal accumulation and toxicity.
From a therapeutic standpoint, maintaining optimal enzyme levels through dietary diversity-incorporating raw, fermented, and enzyme‑rich foods-offers a pragmatic approach to sustaining hormonal health.
Hydration, too, plays a non‑negligible role, as water acts as a solvent and medium for enzymatic reactions, thereby influencing catalytic efficiency.
Stress management cannot be ignored; chronic cortisol elevation can down‑regulate the expression of multiple enzymes, compounding the hormonal dysregulation loop.
In sum, the orchestration of enzymatic functions and hormonal pathways constitutes a symphony of biochemical interactions, each note vital for the overall melody of health.
Neglecting any component-be it dietary substrate, hydration, or stress reduction-risks discord, manifesting as fatigue, mood swings, metabolic derailments, or reproductive anomalies.
Thus, a holistic strategy that prioritizes enzyme support is indispensable for preserving hormonal balance and, by extension, overall well‑being.
Embracing this integrative perspective empowers individuals to proactively address the subtle yet profound impact of enzyme deficiency on the endocrine landscape.
kat gee
November 20, 2024 AT 14:19Nice rundown! Seriously, adding pineapple and papaya is a quick win. And chewing your food? That’s a game‑changer. Keep it simple, stay consistent, and you’ll notice the mood swings mellow out. Let’s keep each other pumped on this enzyme boost!!
Iain Clarke
November 29, 2024 AT 06:39For anyone looking for further guidance, reputable sources such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and peer‑reviewed journals provide detailed information on enzyme functions and hormonal interactions. Consider consulting a registered dietitian or an endocrinologist to tailor dietary changes to your specific needs. Also, reputable databases like PubMed can help you explore the latest research on enzyme deficiencies and treatment options.
Courtney Payton
December 7, 2024 AT 22:59Look, I get the hype but we need to be real‑istic – you cant just eat a avocado and expect your hormones to reset overnight. The science is there, but most of us are stuck in the cycle of quick‑fixes and fad diets. So, while I respect the effort, there’s a lot of nuance missing – people need professional guidance not just a list of superfoods. Anyway, that’s my two cents, hopefully not too annoying.
Muthukumaran Ramalingam
December 16, 2024 AT 15:19Okay so I read the whole thing and honestly it feels like a laundry list of things you already know – eat fruit, drink water, do some exercise. Nothing new, just the same old health advice rebranded. If you want to actually fix hormonal issues you need a doctor, not just a recipe for a smoothie.
Garrett Williams
December 25, 2024 AT 07:39Stay positive and keep moving forward.
joba alex
January 2, 2025 AT 23:59While the article emphasizes “enzyme supplementation,” it neglects the role of gut microbiota‑derived enzymatic activity, which profoundly influences endocrine function via short‑chain fatty acid production and bile acid modulation. Ignoring this axis oversimplifies the biochemical landscape.
Rene Lacey
January 11, 2025 AT 16:19Your thorough analysis of the enzymatic mechanisms involved in hormone synthesis is commendable; however, I would like to point out that the interplay between enzymatic activity and epigenetic regulation also warrants consideration. Recent studies have indicated that DNA methylation patterns can modulate the expression of key enzymes such as aromatase and 21‑hydroxylase, thereby influencing hormonal output. Moreover, the circadian rhythm exerts control over enzymatic expression, suggesting that timing of nutrient intake could be critical for optimizing hormonal balance. In practice, aligning protein‑rich meals with periods of heightened enzymatic activity may enhance hormone synthesis efficiency. Finally, while your practical tips are useful, integrating chronobiological principles could elevate the therapeutic impact of dietary interventions.
johnson mose
January 20, 2025 AT 08:39What a vibrant discussion! I love seeing the blend of science and real‑world tips. Remember, consistency is key – keep those fermented foods coming and watch your energy levels lift. And hey, if you ever need a recipe swap, I’m happy to share my favorite kimchi‑based dressings.
Charmaine De Castro
January 29, 2025 AT 00:59Great insights all around. If you’re curious about specific enzyme‑rich foods, blueberries, kefir, and sprouts are excellent choices. Pair them with regular movement and adequate sleep for a well‑rounded approach to hormonal health.